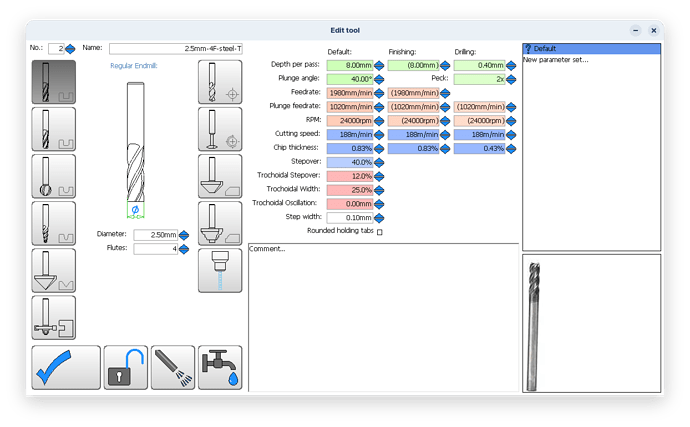
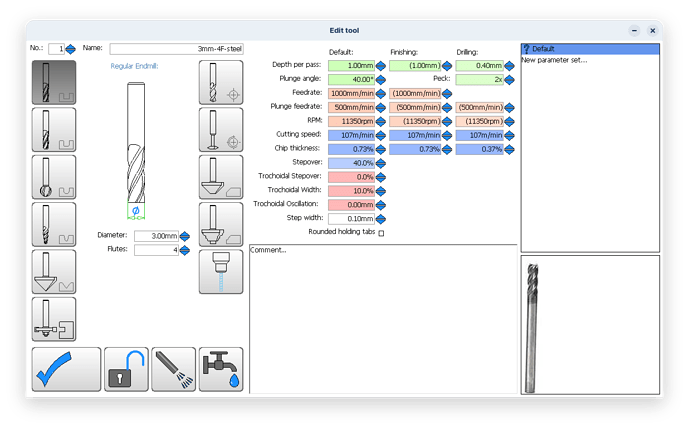
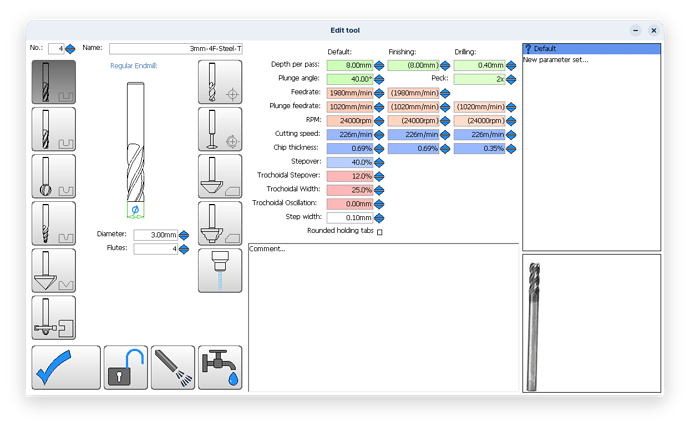
Tool Geometry Basics
Generally, tools with more flutes have a larger core and smaller flute valleys than tools with fewer flutes. More flutes with a larger core can provide both benefits and restrictions depending on the application. Simply put, a larger core is directly proportional to tool strength; the larger the core, the stronger a tool will be. In turn, a larger core also reduces the flute depth of a tool, restricting the amount of space for chips to exist. This can cause issues with chip packing in applications requiring heavy material removal. However, these considerations only lead us part way when making a decision on which tool to use, and when.
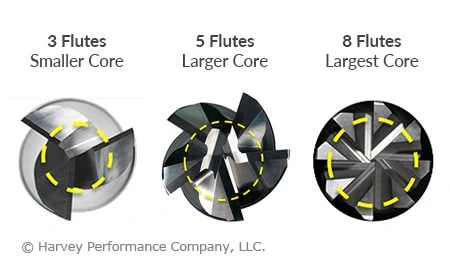
Material Considerations
Traditionally, end mills came in either a 2 flute or 4 flute option. The widely accepted rule of thumb was to use 2 flutes for machining aluminum and non-ferrous materials, and 4 flutes for machining steel and harder alloys. As aluminum and non-ferrous alloys are typically much softer than steels, a tool’s strength is less of a concern, a tool can be fed faster, and larger material removal rates (MRR) is facilitated by the large flute valleys of 2 flute tools.
Consequently, ferrous materials are typically much harder, and require the strength of a larger core. Feed rates are slower, resulting in smaller chips, and allowing for the smaller flute valleys of a larger core tool. This also allows for more flutes to fit on the tool, which in turn increases productivity.

Recently, with more advanced machines and toolpaths, higher flute count tools have become the norm in manufacturing. Non-ferrous tooling has become largely centered on 3 flute tools. This has created a slight advantage over 2 flute tools by increasing productivity while still affording proper chip evacuation. The softness of non-ferrous materials affords a much deeper flute valley. As previously discussed, this allows the tool to be fed much faster than in ferrous materials. Adding an additional flute increases the productivity of the tool, while still affording machinists faster feed rates.
Ferrous tooling has taken a step further and progressed not only to 5 and 6 flutes, but up to 7 flutes and more in some cases. With a wider range of hardness, sometimes at the very top of the Rockwell hardness scale, many more flutes have allowed longer tool life, less tool wear, stronger tools, and less deflection. All of this results in more specialized tools for more specific materials. Material specific tooling combines proper flute counts with coatings that aid in lubricity and heat generation to ensure the most effective end mill possible in the material being machined. The end result is higher MRR and increased productivity across the entire range of ferrous materials that machinists will work with in their shops.