Steve M. Potter’s Portable Primo Build with a Teensy 4.1 MCU plugged into Phil Barrett’s Breakout Board (on Tindie) and running grblHAL firmware
And here is
config.h in two parts because there is a 32000 char limit to these posts.
/*
config.h - compile time configuration and default setting values
Part of grblHAL
Copyright (c) 2020-2022 Terje Io
Grbl is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
(at your option) any later version.
Grbl is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
GNU General Public License for more details.
You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
along with Grbl. If not, see <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>.
*/
// This file contains compile-time configurations for Grbl's internal system. For the most part,
// users will not need to directly modify these, but they are here for specific needs, i.e.
// performance tuning or adjusting to non-typical machines.
// IMPORTANT: Any changes here requires a full re-compiling of the source code to propagate them.
// A reset of non-volatile storage with $RST=* after reflashing is also required as
// most are just default values for settings.
#ifndef _GRBL_CONFIG_H_
#define _GRBL_CONFIG_H_
// Compile time only default configuration
#ifndef N_AXIS
/*! Defines number of axes supported - minimum 3, maximum 6
If more than 3 axes are configured a compliant driver and map file is needed.
*/
#define N_AXIS 3 // Number of axes
#endif
#ifndef COMPATIBILITY_LEVEL
/*! Define compatibility level with the grbl 1.1 protocol.
Additional G- and M-codes are not disabled except when level is set to >= 10.
This does not apply to G- and M-codes dependent on driver and/or configuration settings disabled by setting level > 1.
<br>Set to 0 for reporting itself as "GrblHAL" with protocol extensions enabled.
<br>Set to 1 to disable some extensions, and for reporting itself as "Grbl".
<br>Set to 2 to disable new settings as well, use #define parameters for setting default values.
<br>These can be found in in this file and in defaults.h.
<br>Set to 10 to also disable new coordinate system offsets (G59.1 - G59.3) and some $# report extensions.
__NOTE:__ if switching to a level > 1 please reset non-volatile storage with \a $RST=* after reflashing!
*/
#define COMPATIBILITY_LEVEL 0
#endif
//#define KINEMATICS_API // Remove comment to add HAL entry points for custom kinematics
// Enable Maslow router kinematics.
// Experimental - testing required and homing needs to be worked out.
//#define MASLOW_ROUTER // Default disabled. Uncomment to enable.
// Enable wall plotter kinematics.
// Experimental - testing required and homing needs to be worked out.
//#define WALL_PLOTTER // Default disabled. Uncomment to enable.
// Enable CoreXY kinematics. Use ONLY with CoreXY machines.
// IMPORTANT: If homing is enabled, you must reconfigure the homing cycle #defines above to
// #define HOMING_CYCLE_0 X_AXIS_BIT and #define HOMING_CYCLE_1 Y_AXIS_BIT
// NOTE: This configuration option alters the motion of the X and Y axes to principle of operation
// defined at (http://corexy.com/theory.html). Motors are assumed to positioned and wired exactly as
// described, if not, motions may move in strange directions. Grbl requires the CoreXY A and B motors
// have the same steps per mm internally.
//#define COREXY // Default disabled. Uncomment to enable.
// Add a short delay for each block processed in Check Mode to
// avoid overwhelming the sender with fast reply messages.
// This is likely to happen when streaming is done via a protocol where
// the speed is not limited to 115200 baud. An example is native USB streaming.
//#define CHECK_MODE_DELAY 2 // ms
// After the safety door switch has been toggled and restored, this setting sets the power-up delay
// between restoring the spindle and coolant and resuming the cycle.
#define SAFETY_DOOR_SPINDLE_DELAY 5.0f // Float (seconds)
#define SAFETY_DOOR_COOLANT_DELAY 1.0f // Float (seconds)
/*! @name Control signals bit definitions and mask.
__NOTE:__ these definitions are only referenced in this file. Do __NOT__ change!
*/
///@{
#define SIGNALS_RESET_BIT (1<<0)
#define SIGNALS_FEEDHOLD_BIT (1<<1)
#define SIGNALS_CYCLESTART_BIT (1<<2)
#define SIGNALS_SAFETYDOOR_BIT (1<<3)
#define SIGNALS_BLOCKDELETE_BIT (1<<4)
#define SIGNALS_STOPDISABLE_BIT (1<<5)
#define SIGNALS_ESTOP_BIT (1<<6)
#define SIGNALS_PROBE_CONNECTED_BIT (1<<7)
#define SIGNALS_MOTOR_FAULT_BIT (1<<8)
#define SIGNALS_BITMASK (SIGNALS_RESET_BIT|SIGNALS_FEEDHOLD_BIT|SIGNALS_CYCLESTART_BIT|SIGNALS_SAFETYDOOR_BIT|SIGNALS_BLOCKDELETE_BIT|SIGNALS_STOPDISABLE_BIT|SIGNALS_ESTOP_BIT|SIGNALS_PROBE_CONNECTED_BIT|SIGNALS_MOTOR_FAULT_BIT)
///@}
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// ADVANCED CONFIGURATION OPTIONS:
// Enables code for debugging purposes. Not for general use and always in constant flux.
// #define DEBUG // Uncomment to enable. Default disabled.
// #define DEBUGOUT 0 // Uncomment to claim serial port with given instance number and add HAL entry point for debug output.
// If spindle RPM is set by high-level commands to a spindle controller (eg. via Modbus) or the driver supports closed loop
// spindle RPM control either uncomment the #define SPINDLE_RPM_CONTROLLED below or add SPINDLE_RPM_CONTROLLED as predefined symbol
// on the compiler command line. This will send spindle speed as a RPM value instead of a PWM value to the driver.
//#define SPINDLE_RPM_CONTROLLED
// Some status report data isn't necessary for realtime, only intermittently, because the values don't
// change often. The following macros configures how many times a status report needs to be called before
// the associated data is refreshed and included in the status report. However, if one of these value
// changes, Grbl will automatically include this data in the next status report, regardless of what the
// count is at the time. This helps reduce the communication overhead involved with high frequency reporting
// and agressive streaming. There is also a busy and an idle refresh count, which sets up Grbl to send
// refreshes more often when its not doing anything important. With a good GUI, this data doesn't need
// to be refreshed very often, on the order of a several seconds.
// NOTE: WCO refresh must be 2 or greater. OVERRIDE refresh must be 1 or greater.
//#define REPORT_OVERRIDE_REFRESH_BUSY_COUNT 20 // (1-255)
//#define REPORT_OVERRIDE_REFRESH_IDLE_COUNT 10 // (1-255) Must be less than or equal to the busy count
//#define REPORT_WCO_REFRESH_BUSY_COUNT 30 // (2-255)
//#define REPORT_WCO_REFRESH_IDLE_COUNT 10 // (2-255) Must be less than or equal to the busy count
// The temporal resolution of the acceleration management subsystem. A higher number gives smoother
// acceleration, particularly noticeable on machines that run at very high feedrates, but may negatively
// impact performance. The correct value for this parameter is machine dependent, so it's advised to
// set this only as high as needed. Approximate successful values can widely range from 50 to 200 or more.
// NOTE: Changing this value also changes the execution time of a segment in the step segment buffer.
// When increasing this value, this stores less overall time in the segment buffer and vice versa. Make
// certain the step segment buffer is increased/decreased to account for these changes.
//#define ACCELERATION_TICKS_PER_SECOND 100
// Sets the maximum step rate allowed to be written as a Grbl setting. This option enables an error
// check in the settings module to prevent settings values that will exceed this limitation. The maximum
// step rate is strictly limited by the CPU speed and will change if something other than an AVR running
// at 16MHz is used.
// NOTE: For now disabled, will enable if flash space permits.
//#define MAX_STEP_RATE_HZ 30000 // Hz
// With this enabled, Grbl sends back an echo of the line it has received, which has been pre-parsed (spaces
// removed, capitalized letters, no comments) and is to be immediately executed by Grbl. Echoes will not be
// sent upon a line buffer overflow, but should for all normal lines sent to Grbl. For example, if a user
// sendss the line 'g1 x1.032 y2.45 (test comment)', Grbl will echo back in the form '[echo: G1X1.032Y2.45]'.
// NOTE: Only use this for debugging purposes!! When echoing, this takes up valuable resources and can effect
// performance. If absolutely needed for normal operation, the serial write buffer should be greatly increased
// to help minimize transmission waiting within the serial write protocol.
//#define REPORT_ECHO_LINE_RECEIVED // Default disabled. Uncomment to enable.
// Sets which axis the tool length offset is applied. Assumes the spindle is always parallel with
// the selected axis with the tool oriented toward the negative direction. In other words, a positive
// tool length offset value is subtracted from the current location.
//#define TOOL_LENGTH_OFFSET_AXIS Z_AXIS // Default z-axis. Valid values are X_AXIS, Y_AXIS, or Z_AXIS.
// Minimum planner junction speed. Sets the default minimum junction speed the planner plans to at
// every buffer block junction, except for starting from rest and end of the buffer, which are always
// zero. This value controls how fast the machine moves through junctions with no regard for acceleration
// limits or angle between neighboring block line move directions. This is useful for machines that can't
// tolerate the tool dwelling for a split second, i.e. 3d printers or laser cutters. If used, this value
// should not be much greater than zero or to the minimum value necessary for the machine to work.
//#define MINIMUM_JUNCTION_SPEED 0.0f // (mm/min)
// Sets the minimum feed rate the planner will allow. Any value below it will be set to this minimum
// value. This also ensures that a planned motion always completes and accounts for any floating-point
// round-off errors. Although not recommended, a lower value than 1.0 mm/min will likely work in smaller
// machines, perhaps to 0.1mm/min, but your success may vary based on multiple factors.
// #define MINIMUM_FEED_RATE 1.0f // (mm/min)
// Number of arc generation iterations by small angle approximation before exact arc trajectory
// correction with expensive sin() and cos() calculations. This parameter maybe decreased if there
// are issues with the accuracy of the arc generations, or increased if arc execution is getting
// bogged down by too many trig calculations.
//#define N_ARC_CORRECTION 12 // Integer (1-255)
// The arc G2/3 g-code standard is problematic by definition. Radius-based arcs have horrible numerical
// errors when arc at semi-circles(pi) or full-circles(2*pi). Offset-based arcs are much more accurate
// but still have a problem when arcs are full-circles (2*pi). This define accounts for the floating
// point issues when offset-based arcs are commanded as full circles, but get interpreted as extremely
// small arcs with around machine epsilon (1.2e-7rad) due to numerical round-off and precision issues.
// This define value sets the machine epsilon cutoff to determine if the arc is a full-circle or not.
// NOTE: Be very careful when adjusting this value. It should always be greater than 1.2e-7 but not too
// much greater than this. The default setting should capture most, if not all, full arc error situations.
//#define ARC_ANGULAR_TRAVEL_EPSILON 5E-7f // Float (radians)
// Default constants for G5 Cubic splines
//
//#define BEZIER_MIN_STEP 0.002f
//#define BEZIER_MAX_STEP 0.1f
//#define BEZIER_SIGMA 0.1f
// Time delay increments performed during a dwell. The default value is set at 50ms, which provides
// a maximum time delay of roughly 55 minutes, more than enough for most any application. Increasing
// this delay will increase the maximum dwell time linearly, but also reduces the responsiveness of
// run-time command executions, like status reports, since these are performed between each dwell
// time step.
//#define DWELL_TIME_STEP 50 // Integer (1-255) (milliseconds)
// The number of linear motions in the planner buffer to be planned at any give time. The vast
// majority of RAM that Grbl uses is based on this buffer size. Only increase if there is extra
// available RAM, like when re-compiling for MCU with ample amounts of RAM. Or decrease if the MCU begins to
// crash due to the lack of available RAM or if the CPU is having trouble keeping up with planning
// new incoming motions as they are executed.
// #define BLOCK_BUFFER_SIZE 36 // Uncomment to override default in planner.h.
// Governs the size of the intermediary step segment buffer between the step execution algorithm
// and the planner blocks. Each segment is set of steps executed at a constant velocity over a
// fixed time defined by ACCELERATION_TICKS_PER_SECOND. They are computed such that the planner
// block velocity profile is traced exactly. The size of this buffer governs how much step
// execution lead time there is for other Grbl processes have to compute and do their thing
// before having to come back and refill this buffer, currently at ~50msec of step moves.
// #define SEGMENT_BUFFER_SIZE 10 // Uncomment to override default in stepper.h.
// Configures the position after a probing cycle during Grbl's check mode. Disabled sets
// the position to the probe target, when enabled sets the position to the start position.
// #define SET_CHECK_MODE_PROBE_TO_START // Default disabled. Uncomment to enable.
// Force Grbl to check the state of the hard limit switches when the processor detects a pin
// change inside the hard limit ISR routine. By default, Grbl will trigger the hard limits
// alarm upon any pin change, since bouncing switches can cause a state check like this to
// misread the pin. When hard limits are triggered, they should be 100% reliable, which is the
// reason that this option is disabled by default. Only if your system/electronics can guarantee
// that the switches don't bounce, we recommend enabling this option. This will help prevent
// triggering a hard limit when the machine disengages from the switch.
// NOTE: This option has no effect if SOFTWARE_DEBOUNCE is enabled.
// #define HARD_LIMIT_FORCE_STATE_CHECK // Default disabled. Uncomment to enable.
// Adjusts homing cycle search and locate scalars. These are the multipliers used by Grbl's
// homing cycle to ensure the limit switches are engaged and cleared through each phase of
// the cycle. The search phase uses the axes max-travel setting times the SEARCH_SCALAR to
// determine distance to look for the limit switch. Once found, the locate phase begins and
// uses the homing pull-off distance setting times the LOCATE_SCALAR to pull-off and re-engage
// the limit switch.
// NOTE: Both of these values must be greater than 1.0 to ensure proper function.
// #define HOMING_AXIS_SEARCH_SCALAR 1.5f // Uncomment to override defaults in limits.c.
// #define HOMING_AXIS_LOCATE_SCALAR 10.0f // Uncomment to override defaults in limits.c.
// Enable the '$RST=*', '$RST=$', and '$RST=#' non-volatile storage restore commands. There are cases where
// these commands may be undesirable. Simply comment the desired macro to disable it.
// NOTE: See SETTINGS_RESTORE_ALL macro for customizing the `$RST=*` command.
//#define DISABLE_RESTORE_NVS_WIPE_ALL // '$RST=*' Default enabled. Uncomment to disable.
//#define DISABLE_RESTORE_NVS_DEFAULT_SETTINGS // '$RST=$' Default enabled. Uncomment to disable.
//#define DISABLE_RESTORE_NVS_CLEAR_PARAMETERS // '$RST=#' Default enabled. Uncomment to disable.
//#define DISABLE_RESTORE_DRIVER_PARAMETERS // '$RST=&' Default enabled. Uncomment to disable. For drivers that implements non-generic settings.
// Defines the non-volatile data restored upon a settings version change and `$RST=*` command. Whenever the
// the settings or other non-volatile data structure changes between Grbl versions, Grbl will automatically
// wipe and restore the non-volatile data. These macros controls what data is wiped and restored. This is useful
// particularily for OEMs that need to retain certain data. For example, the BUILD_INFO string can be
// written into non-volatile storage via a separate program to contain product data. Altering these
// macros to not restore the build info non-volatile storage will ensure this data is retained after firmware upgrades.
//#define SETTINGS_RESTORE_DEFAULTS 0 // Default enabled, uncomment to disable
//#define SETTINGS_RESTORE_PARAMETERS 0 // Default enabled, uncomment to disable
//#define SETTINGS_RESTORE_STARTUP_LINES 0 // Default enabled, uncomment to disable
//#define SETTINGS_RESTORE_BUILD_INFO 0 // Default enabled, uncomment to disable
//#define SETTINGS_RESTORE_DRIVER_PARAMETERS 0 // Default enabled, uncomment to disable
// Enable the '$I=(string)' build info write command. If disabled, any existing build info data must
// be placed into non-volatile storage via external means with a valid checksum value. This macro option is useful
// to prevent this data from being over-written by a user, when used to store OEM product data.
// NOTE: If disabled and to ensure Grbl can never alter the build info line, you'll also need to enable
// the SETTING_RESTORE_ALL macro above and remove SETTINGS_RESTORE_BUILD_INFO from the mask.
// NOTE: See the included grblWrite_BuildInfo.ino example file to write this string seperately.
// #define DISABLE_BUILD_INFO_WRITE_COMMAND // '$I=' Default enabled. Uncomment to disable.
// Enables and configures Grbl's sleep mode feature. If the spindle or coolant are powered and Grbl
// is not actively moving or receiving any commands, a sleep timer will start. If any data or commands
// are received, the sleep timer will reset and restart until the above condition are not satisfied.
// If the sleep timer elaspes, Grbl will immediately execute the sleep mode by shutting down the spindle
// and coolant and entering a safe sleep state. If parking is enabled, Grbl will park the machine as
// well. While in sleep mode, only a hard/soft reset will exit it and the job will be unrecoverable.
// NOTE: Sleep mode is a safety feature, primarily to address communication disconnect problems. To
// keep Grbl from sleeping, employ a stream of '?' status report commands as a connection "heartbeat".
//#define SLEEP_ENABLE // Default disabled. Uncomment to enable.
//#define SLEEP_DURATION 5.0f // Number of minutes before sleep mode is entered.
// Disable non-volatile storage emulation/buffering in RAM (allocated from heap)
// Can be used for MCUs with no non-volatile storage or as buffer in order to avoid writing to
// non-volatile storage when not in idle state.
// The buffer will be written to non-volatile storage when in idle state.
//#define BUFFER_NVSDATA_DISABLE
//#define ENABLE_BACKLASH_COMPENSATION
// End compile time only default configuration
// When the HAL driver supports spindle sync then this option sets the number of pulses per revolution
// for the spindle encoder. Depending on the driver this may lead to the "spindle at speed" detection
// beeing enabled. When this is enabled grbl will wait for the spindle to reach the programmed speed
// before continue processing. NOTE: Currently there is no timeout for this wait.
// Default value is 0, meaning spindle sync is disabled
//#define DEFAULT_SPINDLE_PPR 0 // Pulses per revolution. Default 0.
// This option will automatically disable the laser during a feed hold by invoking a spindle stop
// override immediately after coming to a stop. However, this also means that the laser still may
// be reenabled by disabling the spindle stop override, if needed. This is purely a safety feature
// to ensure the laser doesn't inadvertently remain powered while at a stop and cause a fire.
//#define DEFAULT_ENABLE_LASER_DURING_HOLD // Default enabled. Uncomment to disable.
// This option is for what should happen on resume from feed hold.
// Default action is to restore spindle and coolant status (if overridden), this contradicts the
// behaviour of industrial controllers but is in line with earlier versions of Grbl.
//#define DEFAULT_NO_RESTORE_AFTER_FEED_HOLD // Default enabled. Uncomment to disable.
// When Grbl powers-cycles or is hard reset with the MCU reset button, Grbl boots up with no ALARM
// by default. This is to make it as simple as possible for new users to start using Grbl. When homing
// is enabled and a user has installed limit switches, Grbl will boot up in an ALARM state to indicate
// Grbl doesn't know its position and to force the user to home before proceeding. This option forces
// Grbl to always initialize into an ALARM state regardless of homing or not. This option is more for
// OEMs and LinuxCNC users that would like this power-cycle behavior.
//#define DEFAULT_FORCE_INITIALIZATION_ALARM // Default disabled. Uncomment to enable.
// At power-up or a reset, Grbl will check the limit switch states to ensure they are not active
// before initialization. If it detects a problem and the hard limits setting is enabled, Grbl will
// simply message the user to check the limits and enter an alarm state, rather than idle. Grbl will
// not throw an alarm message.
//#define DEFAULT_CHECK_LIMITS_AT_INIT // Default disabled. Uncomment to enable.
// Configure options for the parking motion, if enabled.
#define DEFAULT_PARKING_AXIS Z_AXIS // Define which axis that performs the parking motion
#define DEFAULT_PARKING_TARGET -5.0f // Parking axis target. In mm, as machine coordinate [-max_travel,0].
#define DEFAULT_PARKING_RATE 2500.0f // Parking fast rate after pull-out in mm/min.
#define DEFAULT_PARKING_PULLOUT_RATE 600.0f // Pull-out/plunge slow feed rate in mm/min.
#define DEFAULT_PARKING_PULLOUT_INCREMENT 10.0f // Spindle pull-out and plunge distance in mm. Incremental distance.
// Must be positive value or equal to zero.
// Enables a special set of M-code commands that enables and disables the parking motion.
// These are controlled by `M56`, `M56 P1`, or `M56 Px` to enable and `M56 P0` to disable.
// The command is modal and will be set after a planner sync. Since it is g-code, it is
// executed in sync with g-code commands. It is not a real-time command.
// NOTE: PARKING_ENABLE is required. By default, M56 is active upon initialization. Use
// DEACTIVATE_PARKING_UPON_INIT to set M56 P0 as the power-up default.
//#define DEFAULT_ENABLE_PARKING_OVERRIDE_CONTROL // Default disabled. Uncomment to enable
//#define DEFAULT_DEACTIVATE_PARKING_UPON_INIT // Default disabled. Uncomment to enable.
// Using printable ASCII characters for realtime commands can cause issues with
// files containing such characters in comments or settings. If the GCode sender support the
// use of the top-bit set alternatives for these then they may be disabled.
// NOTE: support for the top-bit set alternatives is always enabled.
// NOTE: when disabled they are still active outside of comments and $ settings
// allowing their use from manual input, eg. from a terminal or MDI.
//#define DEFAULT_NO_LEGACY_RTCOMMANDS // Default disabled. Uncomment to enable.
//#define DEFAULT_TOOLCHANGE_MODE 0 // 0 = Normal mode, 1 = Manual change, 2 = Manual change @ G59.3, 3 = Manual change and probe sensor @ G59.3 - sets TLO
//#define DEFAULT_TOOLCHANGE_PROBING_DISTANCE 30 // max probing distance in mm for mode 3
//#define DEFAULT_TOOLCHANGE_FEED_RATE 25.0f // mm/min
//#define DEFAULT_TOOLCHANGE_SEEK_RATE 200.0f // mm/min
//#define DEFAULT_TOOLCHANGE_PULLOFF_RATE 200.0f // mm/min
Continued in next post…
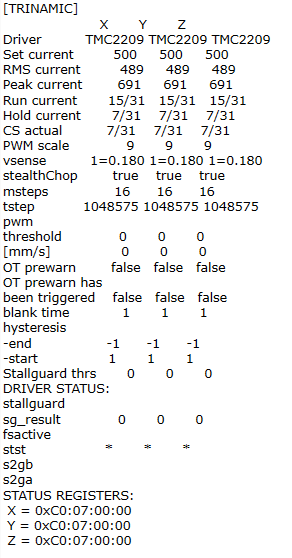
 fedeback can be shared here :
fedeback can be shared here :